Tantaline®

Tantaline® is a special surface treatment, through which stainless steel parts are given the extensive corrosion resistant properties of tantalum. Special rare metals such as nickel alloys, titanium, zirconium, niobium and even tantalum can be replaced by Tantaline®.
Tantaline® treatment is a diffusion bonded protective layer of tantalum, formed by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) on the surface of common materials. The proprietary process creates a dense tantalum surface with all the beneficial properties of pure tantalum. The Tantaline® process is conducted in a sealed reaction chamber under highly controlled conditions. The resulting surface has the same properties as pure tantalum. Due to its very dense surface oxide layer, tantalum is the most corrosion resistant metal commercially available. It has been well established in industrial applications, under high temperature acidic environments.
Der eigene Prozess erzeugt eine extrem dichte Oberfläche aus Tantal mit allen vorteilhaften Eigenschaften von reinem Tantal. Das Tantaline® Verfahren wird in einer geschlossenen Reaktionskammer unter sehr kontrollierten Bedingungen durchgeführt.
If you are interested in our products, please have a look in our (printable) brochure.
Applications
Applications
Typical parts treated by Tantaline® are valves, fittings, autoclaves, process chambers, flow reactors, bellows, fasteners, flowmeters,
mixers, custom parts, medical devices and many other items.
Please contact us with your special request.

Characteristics of Tantaline® Surface Alloy

Characteristics
•Diffusion bonded and inseparable to the base part
•Thickness of tantalum layer is 50 μm
•Treatment of large and small parts
•100% dense layer
•Geometry independent
Hardness
Tantaline® has a hardness similar to SuS 316
•Brinell @3000kg: 193 - 2 40
•Measured 200 - 250 Vickers
•Rockwell C: 11 - 23
•Rockwell B : 92 - 100
•Rockwell A: 56 - 62
Properties of Tantaline® treated components
Properties
Tantaline ® has a unique combination of mechanical properties and characteristics, that allow treated components to service extremely severe environments. Tantaline ® treated components are rugged, durable, ductile and of course corrosion resistant.
The secret to the Tantaline ® solution is its long service life, rapid turn-around and cost-effective pricing.
Thermal Shock Resistance
After every Tantaline ® treatment, the following test is executed:
•Samples are water quenched from 300°C
•48h corrosion test 32% HCl at 75°C after 10–30–60–100 cycles
Result after 100 cycles:
•No cracks, delamination or other defects observed
•No corrosion observed

Testcoupon

Request test coupon
The ring on the left side is a 316 stainless steel washer that has been treated in the Tantaline® process .
We offer this test coupon to test in your corrosive
medium.
Please contact us for further information.
Dimensions of washer: D30mm x 2,5mm
Application notes
Using the link on the right you can view our application notes. In these notes the properties of Tantaline® are explained with components that are often provided by the Tantaline® treatment.
Corrosion table
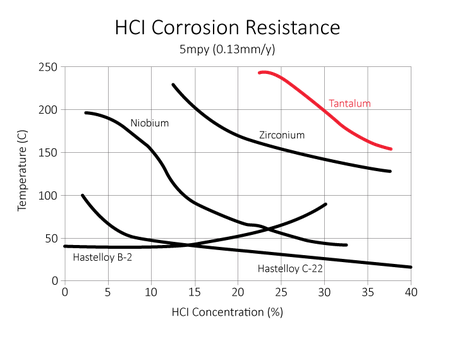
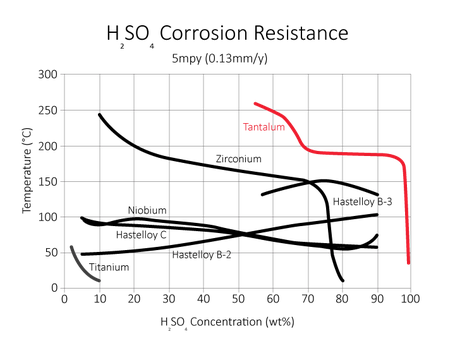
Corrosion table
Tantaline is resistant against corrosion with the following media up to 150 degrees Celsius, unless stated otherwise.

|
Acetic acid |
Ethyl sulfate |
Phosphorus, <700°C (1290°F) |
|
Acetic anhydride |
Ferric chloride |
Phosphorus chlorides |
|
Acetone |
Ferric sulfate |
Phosphorus oxychloride |
|
Air, <300°C (570°F) |
Ferrous sulfate |
Pickling acids, except HNO3-HF |
|
Aldehydes |
Formaldehyde |
Potassium bromide |
|
Aluminum chloride |
Formic acid |
Potassium chloride |
|
Aluminum nitrate |
Glycerine |
Potassium dichromate |
|
Aluminum sulfate |
Hydroiodic acid |
Potassium ferricyanide |
|
Amines |
Hydrobromic acid |
Potassium iodine-iodine |
|
Ammonium bicarbonate |
Hydrocarbons |
Potassium nitrate |
|
Ammonium carbonate |
Hydrochloric acid |
Potassium permanganate |
|
Ammonium chloride |
Hydrogen bromide, <400°C |
Potassium sulfate |
|
Ammonium nitrate |
Hydrogen chloride, <350°C |
Propionic acid |
|
Ammonium phosphate |
Hydrogen iodide |
Silver nitrate |
|
Ammonium sulfate |
Hydrogen peroxide |
Sodium acetate |
|
Amyl acetate or chloride |
Hydrogen sulfide |
Sodium aluminate |
|
Aniline hydrochloride |
Hydroxyacetic acid |
Sodium bisulfate, solution |
|
Barium carbonate |
Hypochlorus acid |
Sodium bromide |
|
Barium chloride |
Iodine, <300°C (570°F) |
Sodium chlorate |
|
Barium hydroxide |
Ketones |
Sodium chloride |
|
Barium nitrate |
Lactic acid |
Sodium citrate |
|
Benzoic acid |
Magnesium chloride |
Sodium cyanide |
|
Boric acid |
Magnesium hydroxide |
Sodium dichromate |
|
Bromine, dry, <300°C (570°F) |
Magnesium sulfate |
Sodium hypochlorite |
|
Bromine, wet |
Manganous chloride |
Sodium nitrate |
|
Butyric acid |
Methyl alcohol |
Sodium nitrite |
|
Calcium bicarbonate |
Methylsulfuric acid |
Sodium phosphate |
|
Calcium bisulfates |
Mineral oils |
Sodium silicate |
|
Calcium bisulfites |
Mixed acids (sulfuric-nitric) |
Sodium sulfate |
|
Calcium carbonate |
Motor fuels |
Sodium sulfide |
|
Calcium chloride |
Nickel salts |
Sodium sulfite |
|
Calcium hydroxide |
Nitric acid |
Sodium thiosulfate |
|
Calcium hypochlorite |
Nitric acid, fuming |
Stearic acid |
|
Carbolic acid |
Nitric oxides |
Succinic acid |
|
Carbon dioxide |
Nitrogen, <300°C (570°F) |
Sulfamic acid |
|
Chloric acid |
Nitrous acid |
Sulfur, <500°C (930°F) |
|
Chlorinated brine |
Nitrosyl chloride |
Sulfur chlorides |
|
Chlorine, dry, <250°C (480°F) |
Organic chlorides |
Sulfur dioxide |
|
Chlorine, wet, <350°C (662°F) |
Organic acids |
Sulfuric acid, to 175°C (350°F) |
|
Chlorine oxides |
Organic esters |
Sulfurous acid |
|
Chloroacetic acid |
Organic salts |
Sulfuryl chloride |
|
Chromic acid |
Oxalic acid |
Tannic acid |
|
Citric acid |
Oxygen, <300°C (570°F) |
Tartaric acid |
|
Copper salts |
Pechloric acid |
Thoinyl chloride |
|
Dichloroacetic acid |
Petroleum products |
Tin salts |
|
Dimethylformaldehyde |
Phenol |
Zinc chloride |
|
Ethylene dibromide |
Phosphoric acid, <4ppmp, <180°C |
Zinc sulphate |
Limited corrosion resistance
Tantaline offers limited corrosion resistance with the following media.
|
Air, >300°C (570°F) |
Oleum (fuming sulfuric acid) |
Sodium carbonate |
|
Ammonia |
Potassium carbonate |
Sodium hydroxide, dilute |
|
Ammonium hydroxide |
Potassium hydroxide, dilute |
Sodium hydroxide, conc. |
|
Fluoride salt |
Potassium hydroxide, conc. |
Sodium pyrosulfate, molten |
|
Hydrofluoric acid |
Potassium pyrosulfate, molten |
Sulfur trioxide |
|
Hydrogen, <300°C (570°F) |
Sodium bisulfate, molten |
Sulfuric acid, >175°C (350°F) |
|
Hydrogen fluoride |
|
|
